Introduction:-
Muscle Relaxation is a an ancient technique which is mainly used for the reduction of muscle spasm, muscle tension in body the body stress which lowers down the cardiovascular rate and promote a sense of well being. In physiotherapy Muscle relaxation can physically done by the physiotherapist with various method such as (MET- Muscle Energy Technique), Stretching, Massage Therapy etc.
Table of Content
★What are Relaxed Muscle?
Muscles which are free from tension and are at rest is said to be Relaxed muscles. Tension develop in muscles as they work during contraction and this tension is reduced to a variable degree as the muscles come to rest during Relaxation. In Relaxed Muscle the body feels more comfortable and free from stiffness, Tightness and pain. Relaxed muscle are achieved when a person is free from mental and physical stress.
Muscle Tone
Generally, living muscle are never completely free from tension because as they retain the quality of firmness (stability) known as muscle tone. Muscle tone represents a state of alert mode in resting muscle. The Efferent fibers of nervous reflex pathway transmit impulse which produce a sustained contraction of small intrafusal muscle fibers of the muscle (muscle fibers which are inside the spindle). While the large extrafusal muscle fibers concerned in the production of Voluntary movement remain relaxed.
Postural Tone
Muscle which is concerned with the maintenance of posture especially (Anti-gravity muscle). It represents the tonic activation of muscles in order to provide specific postural attitude and generate force against the ground to keep the limbs Extended. Any stretching of the muscles by an external force such as:- Force of gravity which stimulates sensory receptors situated within the muscle and give rise to a discharge of motor impulse to the same muscles. Motor impulse brings about a contraction of sufficient number of muscles motor units to increase the tension sufficiently.
As muscle tension increase in response to stretching by an external force (as per the degree of stretching) These postural tone reduce or eliminate the effect of force in promoting relaxation. The degree of Postural tone varies in alternate in posture.
Voluntary Movement
The muscles which can be control voluntarily by the human body. To initiate or control movement then specific should be muscle contract. After completion of movement these muscle come to rest and relaxed because they are under conscious control so a body can easily perform movement when they want to.
Mental Attitudes
Mental attitudes are highly responsible for the stiffness , pain and relaxation Such as fear, anger and excitement give rise to increase or decrease in muscle tension which serves a useful purpose by preparing the muscle for rapid or forceful action. In some cases it becomes habitual and lead to alteration in normal posture. Positive mental attitudes promote good posture, imoroves body alignment and balanced the muscle tone.
DEGREE OF RELAXATION
The degree to which muscle tension is reduced which termed as relaxation. It is often possible to calculate the degree of relaxation is achieved by passive movement or by palpating muscle. (The fact that patient falls as sleep during treatment is a proof that a method of obtaining general relaxation has been successful). There are different stages/Degree of Muscle Relaxation such as:-
- Moderate Relaxation like stretching and meditation technique.
- Deep Relaxation mainly achieved while sleeping peacefully or after the relaxation techniques has been given to the patient.
Pathological tension in muscle
Many pathological condition interrupt in tone of muscle or muscular tension such as affect of Nervous System. Damage in higher motor centers and interfere in normal function of Nervous pathway which connects to Spinal Reflex Arc. It result in abnormal state of muscular tension which causes Hypertonicity to Spasticity or Rigidity. By suitable exercises the tension in affected area can be reduced temporarily which promote Relaxation, and this allows recovery of any functional activity which remain to take place.
General Relaxation
Support, Comfort and restful atmosphere are basic condition for General Relaxation.
Lying Supine
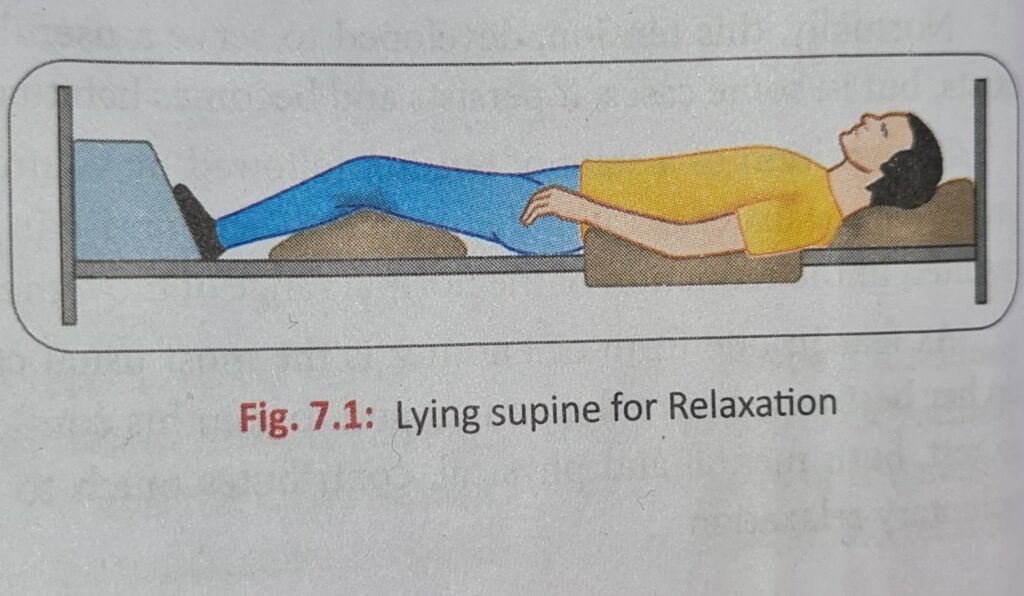
- A firm surface is essential as in case of good spring mattress, it is ideal as it will mould itself to the body contours and give even pressure and comfort.
- Beds which provide discomfort are to be avoided as they cramp the thorax and give additional strain on the inspiratory muscle (Diaphragm).
- A soft head pillow is required to prevent the head from rolling to either side.
- A small pillow under the knees relieves tension on the hamstring and Iliofemoral ligament, as a result it allows pelvis to roll backward so that Lumbar Spine is straightened.
- The feet are held in Mid-Position by a sand bag and similar device on each arm slightly abducted Shoulder and flexed at the elbow
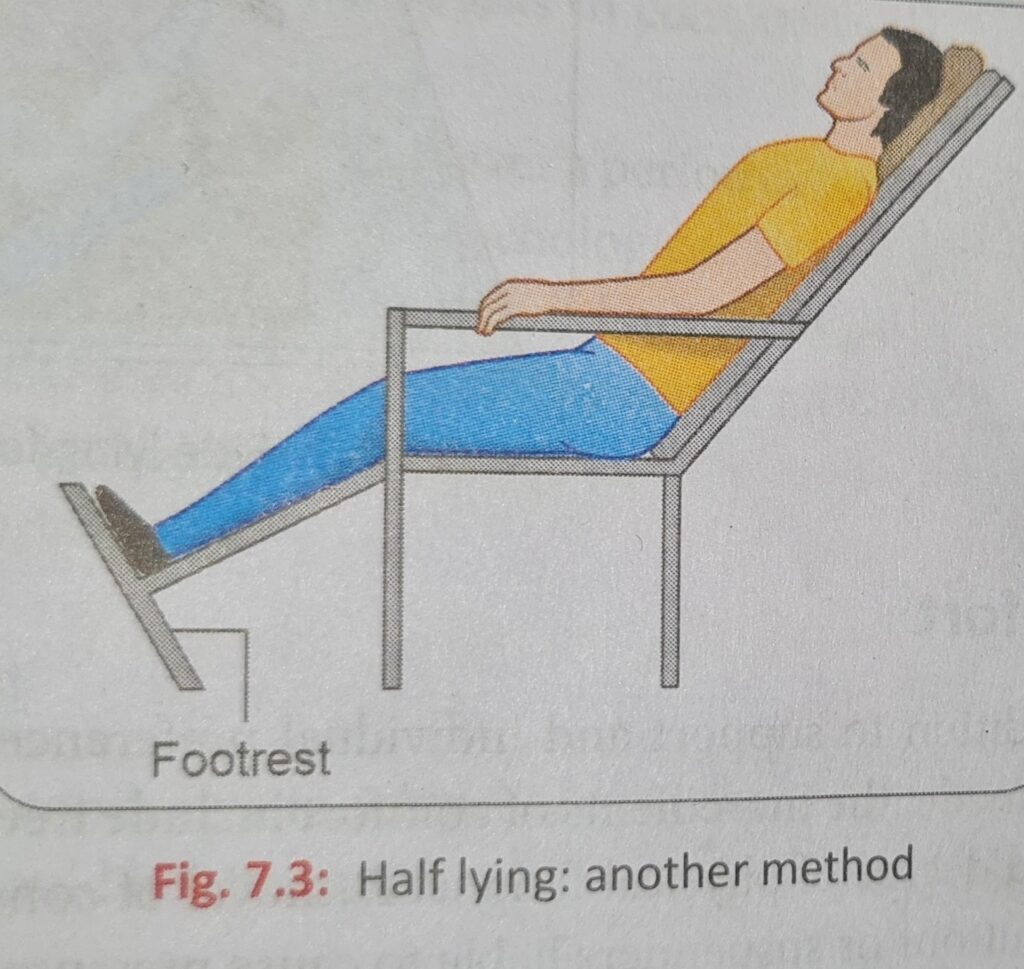
Half Lying
This is similar to the previous position but breathing is easier as there is less weight on the back and abdominal pressure on the under surface of the diaphragm is reduced.
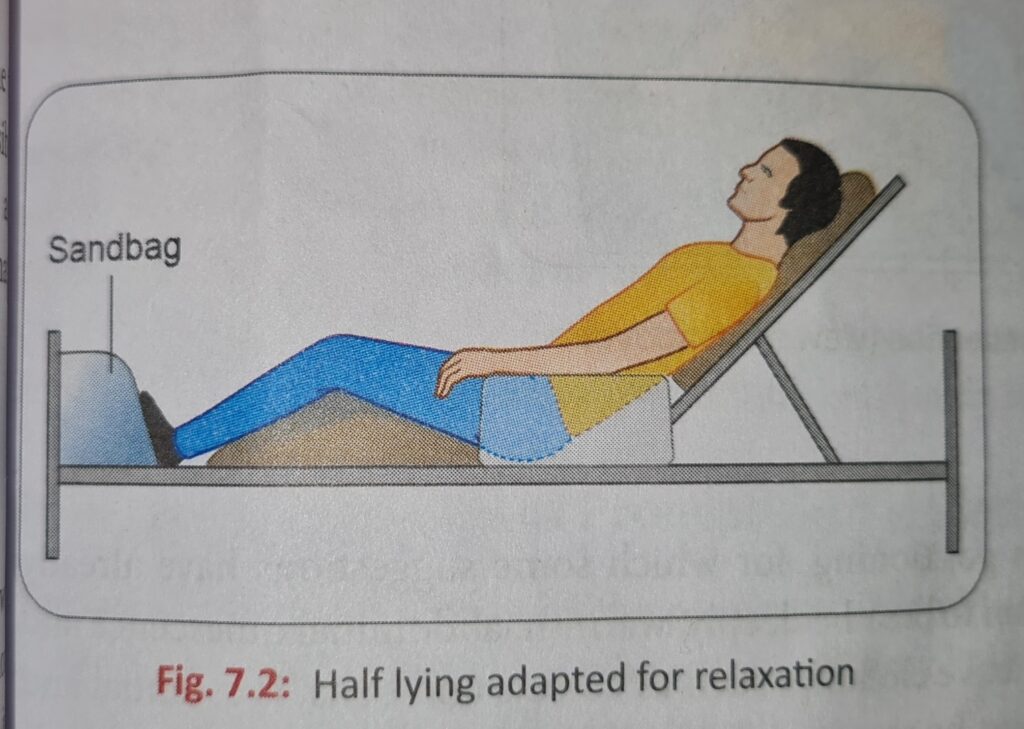
An Arm chair makes a good substitute for a plinth or bed, the thighs are fully supported and the feet rest on the floor.
Prone Lying
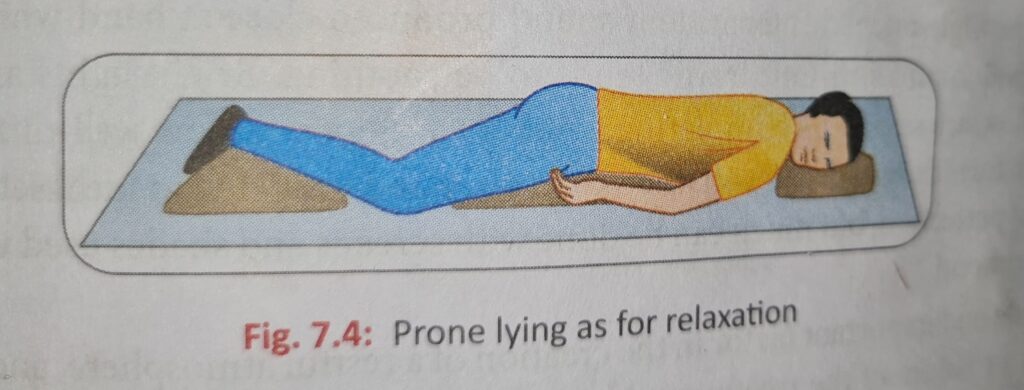
- The head is turn to one side and rest on a small pillow.
- A pillow under the hips and lower abdomen prevents hollowing of the back; For Women it should be avoid higher pressure on the breasts.
- The lower leg is elevated so that the knees are slightly bend and the toes are free.
- Many people find this position comfortable and use it for sleeping.
- Other dislike it because of the rotated position of the head.
Side Lying
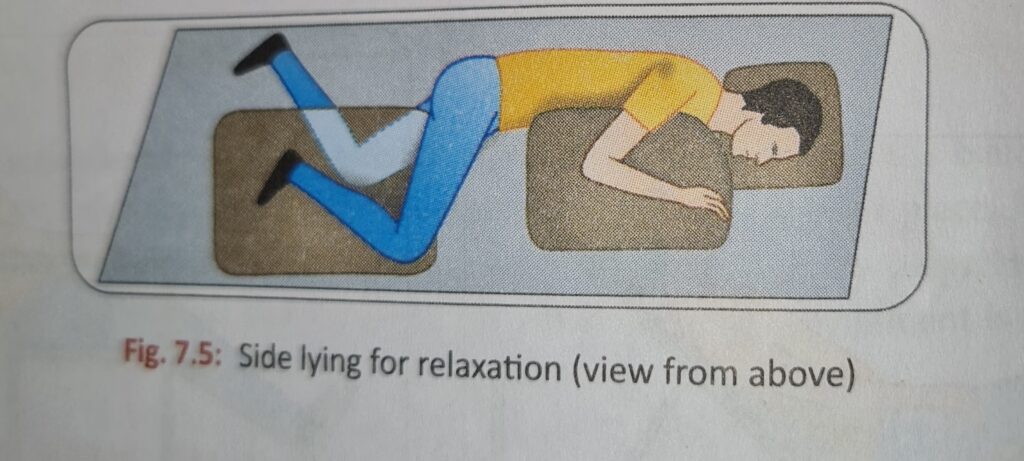
- The relaxation is obtained when the Shoulder and Pelvic Girdle are stable.
- The uppermost arm and leg must be on supporting surfaces.
- The head pillow support the head and neck in alignment with the body and must not ne too high.
- The majority of the people sleep on the side nut only few are conscious of the part that suitable positioning for relaxation.
Preparation of Comfort Zone
- The ingredient of comfort Is freedom to breathe, warmth, abdominal relaxation and physical fatigue.
- Removal of tight cloth such as Belts.
- The warm room and freely fresh air.
- In winter, additional warmth is supplied by light a warm blanket, a hot water bottle at the feet.
- Avoid over heating because it leads to restlessness.
- For home use a warm bath gives the most even and pleasing type. of heat.
- A light well-balanced meal, physical activity for short duration.
- A state of mental rest.
- The room should be quiet as possible.
- A low well-diffused light with green and peach furnishing gives a soft and warm glow provides an ideal setting for relaxation.
- An appearance of physiotherapy must be tidy and suitable dress.
- He/she must be punctual and move calmly.
- They should have low-pitched voice.
- Consciousness of Breathing
Contrast Method
- Difficulty in feeling the sensation of relaxation.
- The patient is unable to feel that the muscles are tensed and what to do in order to relax them.
- This can be taught to the patient by demonstrating the contrast between the maximal contraction and the degree of relaxation.
- For an example, The patient being told to contract any group or series of muscles as strongly as possible and then to let go.
- This method should be continued till the patient is unable to do the contraction and get tired and the state of fatigue is produced.
- Routine contraction is followed in each and every part of the body such as Limb to Limb, Trunk to head including neck and face muscles until all areas is remain relaxed.
- Before the routine is completed the patient is frequently drop off to sleep and a feeling of general relaxation is achieved.
Physiological Relaxation
The position of tension of the whole body is defined as Raised shoulder, bent up elbows and hands, head and trunk are flexed. The patient changes the position in every joint in turn by exact voluntary orders.
Passive Movement
Rhythmical Passive movements of the limbs and head may assists the degree of general relaxation in some cases. Group movements of joints such as :- Flexion, Extension of Hip, knee, ankle but very high standard should be performed by the Physiotherapist to get results.
For a Relief of Spasm
- There are techniques which ensure pain free movements and are often successful.
- Hold and relax is applicable in these situation or pendular movements which start in the free range may achieve relaxation.
- In case of pathological spasm, there is no permanent solution.
- Temporary relief is useful for re-development of voluntary control and to maintain joint range and circulation in affected area.
To learn more about Ultraviolet Radiation click the given link https://physiocontent.com/ultrasound-therapy-ust-principles/
To learn more about TENS- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation https://physiocontent.com/tens-transcutaneous-electrical-nerve-stimulation/
[…] To learn and understand more about Relaxation Technique click the given link https://physiocontent.com/muscle-relaxation-techniques-and-benefits-of-relaxed-muscles/ […]
[…] To learn and understand more about Relaxation Technique click the given link https://physiocontent.com/muscle-relaxation-techniques-and-benefits-of-relaxed-muscles/ […]